Table of Contents
Introduction
Today, email still sits at the center of customer communication. Contracts, invoices, health records, onboarding documents, and support conversations all flow through email.
And when those emails originate from Salesforce, it’s natural to assume the CRM protects the data end-to-end. But are emails sent from Salesforce actually encrypted once they leave Salesforce?
In fact, according to a recent Email Security breach report, 78% of organizations experienced at least one email-related security breach in the past 12 months, reinforcing how vulnerable email remains when encryption and controls are misunderstood or misconfigured.
This blog explains how Salesforce email encryption works, what security applies to outbound emails, where Salesforce's native protections fall short, and how you can secure sensitive communications without disrupting everyday workflows.
How Does Salesforce Handle Email Security and Encryption?
Salesforce email encryption secures outbound emails that contain sensitive customer data. It uses TLS to encrypt the email connection during transmission. TLS protects the transfer session, not end-to-end encryption of the email content.
Administrators control encryption through policy-based rules in Salesforce setup. Encryption protects confidential data sent to external recipients. The feature supports compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Salesforce email encryption works automatically when defined conditions apply. The system integrates with native Salesforce security tools and audit logs. The approach reduces data breach risk without disrupting normal email workflows.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how Salesforce encrypts emails.
1. Encryption in Transit vs Encryption at Rest
Salesforce secures emails differently depending on whether they are being sent or stored.
- Encryption in Transit
When an email is sent from Salesforce to an external recipient, Salesforce attempts to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure the connection. TLS encrypts the connection between Salesforce and the recipient’s mail server, protecting the email from interception while it is in transit. This protection depends on the recipient server supporting TLS.
- Encryption at Rest
Once an email reaches the recipient’s mail server, Salesforce no longer controls how it is stored or accessed. It does not encrypt email content at rest in external inboxes by default, which is a key limitation for teams handling sensitive or regulated data.
Inside Salesforce, data at rest is protected using the platform’s encryption infrastructure. This includes records, files, metadata, and email-related data stored in Salesforce. Using Platform Encryption, Salesforce can encrypt Email Message and Email-to-Case fields, such as subject, body, headers, and email addresses.
This encryption applies only to email records stored within Salesforce and does not extend to emails delivered to external inboxes, which stop being Salesforce-controlled assets after delivery.
2. Email Security Protocols Salesforce Uses
Salesforce relies on several well-established email security protocols to protect delivery and authenticity.
- TLS ensures secure transmission between Salesforce and the recipient’s email server. If the receiving server supports TLS, the email is encrypted during transit. If not, delivery may fall back to an unencrypted connection unless TLS enforcement is configured.
- SPF and DKIM help receiving servers verify that Salesforce is authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain. These protocols reduce spoofing and phishing risks by confirming sender identity. Proper configuration is essential for both security and deliverability.
- DMARC builds on SPF and DKIM by defining how receiving servers should handle emails that fail authentication checks. Salesforce supports DMARC alignment, allowing organizations to set policies that reject or quarantine unauthenticated messages.
These protocols strengthen trust and delivery security, but they do not encrypt the email content itself.
3. Limitations of Salesforce’s Out‑of‑the‑Box Email Encryption
Salesforce’s native email security works well for general communication, but has limitations when handling sensitive or regulated data. Encryption focuses on transmission security rather than full message protection. These key limitations include:
- No native end-to-end encryption for email content
- No encryption at rest for emails stored in external inboxes
- Limited control over how recipients access or store sensitive email data
- Reliance on TLS, which depends on the recipient mail server's support
It’s also important to note that Salesforce does not fully support logging encrypted email messages through Outlook or Gmail integrations.
Using email message encryption with these integrations can lead to unreadable or broken email records inside Salesforce. Teams using encrypted email solutions should validate how email logging and integrations behave before rolling out encryption broadly.
Because of these constraints, organizations with strict compliance or confidentiality requirements often extend Salesforce with external encryption or secure email solutions and look for workable ways to achieve encrypted email delivery in Salesforce.
A similar challenge emerged for Keener Financial Planning, a financial services firm required to send and archive policy documents annually to meet SEC compliance.
After moving to Salesforce, the team discovered that standard Salesforce email tools no longer supported reliable attachment delivery or compliant email archiving. This created a gap between regulatory requirements and Salesforce’s native email capabilities.
By extending Salesforce with MassMailer, Keener was able to securely send attachments, archive emails within Salesforce, and support compliance-driven workflows without relying on external inboxes or manual workarounds.
How to Achieve Encrypted Email Delivery in Salesforce: Key Methods
Achieving encrypted email delivery in Salesforce usually means building on top of native security, not replacing it.
Since Salesforce primarily protects emails during transmission, teams that handle sensitive or regulated data need additional layers to secure email content and attachments beyond delivery.
The right approach depends on how much control is required, what compliance standards apply, and how closely encryption must integrate with existing Salesforce workflows.
There are three common ways organizations extend Salesforce email encryption, each addressing a different level of security and operational complexity.
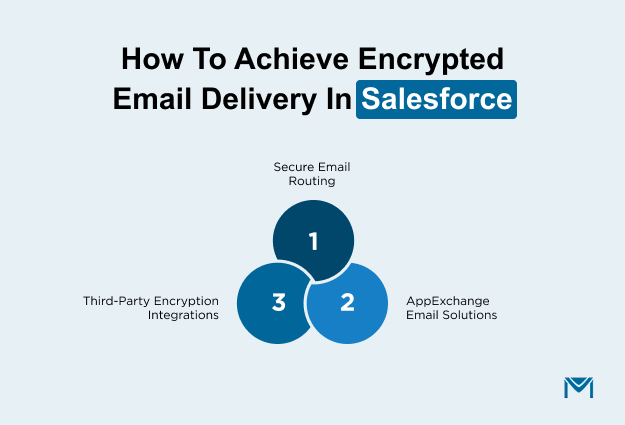
1. Email Relay and Secure Server Routing
Email relay allows Salesforce to route outbound emails through an organization’s secure email infrastructure before delivery.
Instead of sending messages directly to recipients, Salesforce passes them to a designated mail server where additional security controls are applied. This approach works well for organizations that already manage email security centrally. It helps:
- Ensure emails are encrypted during transmission
- Apply consistent security policies across all outbound emails
- Align Salesforce email delivery with existing IT controls
However, email relay still relies on transport-level encryption. While it improves consistency and oversight, it does not always guarantee encryption of email content once messages reach external inboxes.
2. AppExchange Secure Email Solutions
AppExchange secure email solutions take encryption a step further by embedding it directly into Salesforce workflows. These tools encrypt email content and attachments before messages leave Salesforce, reducing reliance on recipient mail server capabilities. This approach is commonly used when:
- TLS alone does not meet compliance requirements
- Teams need encryption without changing user workflows
- Auditability and policy-based controls are required
Solutions like MassMailer are designed for these scenarios. They typically support encrypted storage, recipient authentication, and activity logging, making them suitable for regulated environments without adding operational friction for sales or support teams.
3. Third‑Party Integrations for Encrypted Email
Some organizations integrate Salesforce with dedicated encrypted email providers through APIs or connectors. These tools focus on full message-level encryption and controlled access to sensitive content. This option is often chosen when:
- Regulations require strong encryption at rest and in transit
- Email content must remain encrypted regardless of recipient systems
- Detailed audit trails and access controls are mandatory
While third-party integrations require more setup and governance, they offer the highest level of control over how email content is protected and accessed after delivery.
Once you understand how Salesforce secures emails and where native protections stop, the next step is configuring outbound email settings to ensure secure delivery.
How To Configure Encrypted Outbound Emails in Salesforce?
Configuring encrypted outbound emails in Salesforce starts with strengthening the platform’s native email security controls.
While Salesforce does not provide full message-level encryption by default, proper configuration ensures emails are transmitted securely and trusted by recipient mail servers. These steps form the baseline for secure email delivery and are often required before adding external encryption solutions.
1. Enable TLS Enforcement
Salesforce uses Transport Layer Security to encrypt emails while they are sent between mail servers. By default, Salesforce attempts to use TLS when the recipient’s email server supports it. However, without enforcement, emails may still be delivered over unencrypted connections if TLS is unavailable.
Enabling TLS enforcement ensures that:
- Outbound emails are encrypted during transmission
- Emails are only delivered to servers that support secure connections
- Sensitive data is not sent over unsecured channels
TLS enforcement is configured in Salesforce’s Deliverability settings. This step is especially important for organizations that send confidential or regulated information, as it reduces the risk of interception during delivery. It is also a common requirement during security and compliance reviews.
2. Set up DKIM and SPF records
Encryption alone does not guarantee email security or trust. Salesforce also relies on sender authentication to prove that emails genuinely originate from your organization. This is where DKIM and SPF come in.
SPF defines which servers are authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain. DKIM adds a cryptographic signature to outgoing emails, allowing receiving servers to verify message integrity. Together, they help:
- Prevent email spoofing and impersonation
- Improve email deliverability and reputation
- Build trust with recipient mail servers
Configuring DKIM and SPF records is a foundational security step. Without them, encrypted emails may still be flagged as suspicious or rejected, undermining both security and communication reliability.
Encryption is most valuable in Salesforce when emails involve sensitive or regulated data.
Common Use Cases for Encrypted Emails in Salesforce
Encrypted email in Salesforce usually becomes necessary when routine workflows involve sensitive or regulated data. These scenarios often surface during compliance reviews or security assessments rather than during initial CRM setup.
1. HIPAA and Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Salesforce users in regulated industries such as healthcare, insurance, and financial services regularly send sensitive information through email. Regulations like HIPAA and GDPR require organizations to protect personal data during communication, not just while it is stored.
TLS-based encryption may not be sufficient when emails include attachments or personally identifiable information. Encrypted email solutions help close this gap by protecting email content beyond transmission and supporting audit and compliance requirements.
2. Secure Customer Communications
Salesforce is frequently used to send information that customers expect to remain private, including contracts, financial details, and case updates. Once these emails leave Salesforce, standard email security offers limited protection.
Encryption helps ensure sensitive content remains protected during and after delivery, reduces the risk of unauthorized access, and aligns with customer expectations around privacy. For customer-facing teams, encrypted email provides security without disrupting everyday Salesforce workflows.
Best Practices for Email Encryption in Salesforce
Effective email encryption in Salesforce relies on layering native security controls with consistent configuration. No single setting fully secures outbound emails, but following these best practices significantly reduces risk.

1. Always Enforce TLS for Outbound Emails
TLS protects emails while they are transmitted between mail servers. Enforcing TLS ensures Salesforce only delivers emails over encrypted connections, preventing sensitive data from being sent across unsecured channels. While TLS does not encrypt emails at rest, it remains the minimum requirement for secure outbound communication.
2. Use DKIM and SPF for Sender Authentication
DKIM and SPF confirm that emails sent from Salesforce are authorized and have not been altered. These protocols reduce spoofing and phishing risks while improving email deliverability. Proper authentication is especially important when sending encrypted emails, as it helps recipient servers trust the message source.
3. Use Encrypted Email Tools for Sensitive Data
For regulated or confidential communications, TLS and authentication alone may not be sufficient. Third-party encrypted email tools extend Salesforce’s native security by encrypting message content and attachments before delivery. These tools support stronger confidentiality controls and audit requirements without disrupting standard Salesforce workflows.
Conclusion: Making Salesforce Email More Secure
Salesforce provides a strong foundation for email security, but its native protections have clear limits.
TLS, DKIM, and SPF help secure emails during transmission and verify sender identity, yet they do not ensure that email content remains protected once it leaves Salesforce.
For teams handling sensitive or regulated data, that distinction is critical. This is why many organizations extend Salesforce with encrypted email solutions.
Tools like MassMailer integrate into Salesforce workflows and secure email content and attachments both in transit and at rest. By addressing the limits of native encryption, these solutions help teams protect sensitive communications without adding unnecessary complexity to how Salesforce is used.
If your teams send contracts, financial documents, or regulated customer data from Salesforce, explore how MassMailer offers a practical way to strengthen email security without changing how your teams work.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Salesforce email encryption?
2. How does Salesforce encrypt emails sent to external users?
3. Does Salesforce email encryption work automatically?
4. Is Salesforce email encryption HIPAA or GDPR compliant?
5. Does Salesforce encrypt email attachments?
6. What is the difference between Salesforce email encryption and Salesforce Shield?
Start Your Free Trial Today
Experience MassMailer the easiest way to send personalized emails from Salesforce.
Related Blogs
MassMailer Resources
MassMailer Glossary












